|
Power
Electricity is an essential source of commercial energy. It is vital for sustained economic growth. An increase in demand for power implies growth of the economy leading to modernization, industrialization and improvement in basic amenities culminating into a better quality of life of people. The state of Jammu and Kashmir is endowed with significant hydel potential which, when exploited fully, will provide a strong impetus for the growth of its economy. The estimated hydro power potential of the state is 20,000 Megawatts (MW), of which about 16475 MW have been identified. This comprises 11283 MW in Chenab basin, 3084 MW in Jhelum basin 500 MW in Ravi Basin & 1608 MW in Indus basin. Out of the identified potential, only 2813.46MW i.e. 17 % (of identified potential) has been exploited so far, consisting of 761.96 MW in State Sector from 21 power projects, 2009 MW in Central Sector from 7 projects and MW in private sector from 4 projects .
Potential Harnessed
STATE SECTOR = 761.96 MW
CENTRAL SECTOR = 2009.00 MW
PRIVATE SECTOR = 42.50 MW
TOTAL = 2813.46 MW
Due to resource constraints, exploitation of the potential economic rejuvenator like hydro power has been very steady. Besides, due to the constraints imposed by the provisions of Indus Water Treaty between India and Pakistan preventing water storage of the water of Jhelum, Chenab and Sind rivers, these projects have been constructed as run of the rivers and as such generation reduces to less than 1 / 3rd of installed capacity during winter when the discharge in these snow fed rivers dwindle. The State is therefore perpetually energy deficient and has to rely on power purchase from Northern Grid to meet its requirement particularly in winters, when its own generation recedes and demand peaks. In spite of heavy odds, the State has not wavered from its resolve to ensure electrification of all its villages/hamlets.
The Eighteenth All India Power Survey has projected an increase in power demand of Jammu and Kashmir from 1706 MW i.e. 9640 MUs during 2004-05 to 4217 MW i.e. 21887 MUs during 2021-22.
Power Sector- Strategy, Proposal, Reforms and Concerns
For making the power sector efficient and more competitive, reforms in this sector have been and are underway. While there is some progress, power shortage continues to haunt the State and is a major constraint of the development of the industry and economy. The biggest weakness is on the distribution front. Aggregate
Technical and Commercial (AT&C) losses of our State are about 72 percent. This has posed a major challenge to the fiscal health of the State.
The Eleventh Plan has ensured substantial expansion to move in a comfortable position. Few projects under Central Sector and State Sector have materialized. Capacity of 1946.01 MW has been added from 1996 & 2013-14 in State, Central and Private Sector. Transmission and Distribution network is being strengthened and various measures have been adopted under the reforms. Investment in transmission and distribution infrastructure and restructuring of the APDRP, using technological and managerial tools such as Smart Metering and High Voltage Distribution System (HVDS), tariff monitoring and revision and accountability at each distribution transformer with a goal, are being worked out besides, providing electricity access to all households.
J&K State Electricity Regulatory Commission
The State Government has set up State Electricity Regulatory Commission. The Jammu and Kashmir Power Development Department has already filed four ARR/Tariff petitions with the SERC and SERC has issued tariff orders for 2008-09, 2009-10, 2010-11 and 2011-12. In the present structure, the Generation & transmission continues to be with State's PDC and PDD respectively. In the case of distribution entity, the State Government is proposing to have two discoms one each at Kashmir & Jammu region, besides setting up of separate Transmission Company & Independent SLDC.
Tripartite MOUs
The first MOU was signed in August 2006 between MOF/Planning Commission and Government of J&K. It was agreed that Government of India would provide an amount of Rs.1300 crore (Central assistance) to Jammu and Kashmir Power Development Department (JKPDD) to support the reform initiatives subject to achievement of certain benchmarks which were spelt out in the MoU. The benchmarks were achieved and another MoU was signed in February, 2008. The benchmarks under this MoU were also achieved, except benchmarks of revenue and metering.
Despite several steps of reforms over the years, the situation has not improved much, due to slow pace of progress in distribution segment. Without effective reforms in this area, the sector will not be financially viable and will be unable to achieve the required level of performance. Though some progress has been made for setting up of State Regulatory Organization, yet the actual improvement in distribution is low.
Present Position of Power Generation
During past five decades considerable work has been done in Power Sector within the limitations imposed by the resources and other constraints. The installed capacity in the State, thermal as well as Hydel, is 969.96 MW (208 MW Thermal + 761.96 MW Hydel). The prestigious Baglihar Hydro Electric Project, with a capacity of 450 MW was commissioned during 2008-09. During 2008-09, 2009-10, 2010-11 2011-12 & 2012-13 & 2013-14 1630.115 MUs, 3379.489 MUs, 3647.41 MUs, 3786.434 MUs, 3864.434 MUs of energy was generated respectively from the power projects under operation with JKSPDC. The energy generation for the year 2014-15 is estimated to be 3927.714 MUs.
The aggregate capacity of 761.96 MW hydel power in the State Sector is available to the State, which is helping the State to overcome the power scarcity to some extent.
The machines of the old power houses have outlived their lives in most of the stations and require renovation and modernization. The upper Sindh Hydel Project- II with an installed capacity of 105MW (35x3 MW) was being operated for a capacity of 70 MW only due to reduced availability of water as result of damages to Wangath Link Canal. The construction of an alternate tunnel water conductor has been taken up as per the advice of CWC for restoration of the Project to its design capacity of MW. Work is expected to be completed by August, 2015.
In the Central sector, during the first year of 11th Five Year Plan i.e. 2007-08, Dulhasti Power Project, Kishtwar with the capacity of 390 MW and 120 MW Sewa II were commissioned which increased the power generation in central sector from 1170 MW to 1680 MW. Further during 2013-14, 45 MW Nimo Bazgo, 44 MW Chutak & 2 units of 240 MW Uri II were commissioned increasing the installed capacity of Central Sector Projects to 2009 MW. This capacity stabilizes the State Power situation as State has entitlement of 12 percent free power from these projects.
Besides, the generation of power from the State owned power houses; the State is also entitled to receive the power from Centre Power Sector, as part of power generated by various power houses in the State and outside the State. This is regulated by the Ministry of Power, Government of India and the State has a firm allocation of around 1437 MW including 12% free power from NHPC's power houses of Salal, Uri and Dulhusti. Besides, a share of 617 MW (non-firm share) from unallocated quota which varies from time to time. State as such, has total share of 2054 MW (1437MW firm & 617 MW non-firm)from these stations but the effective availability depends upon the condition of machines, river discharge and the fuel availability.
State Sector Projects under execution
The State Govt. is putting sustained efforts to exploit the power for the economic growth of the state. Under this sector Baglihar Hydro Electric Project-I with an installed capacity of 450.00 MW has been made operational during 2008-09, 1.26 MW Sanjak MHP has been commissioned in 2011 and Capacity of Bhaderwah MHP has been augmented by 0.5 MW in 2011. Further, capacity of Pahalgam MHP has also been augmented by 1.5 MW in 2013. 450 MW BHEP-II is expected to start generation in 2015-16.
Allocation of Coal Block for Setting up of 660 MW Thermal Project
JKSPDC has been allocated coal block (Kudnali Laburi in Odisha ) jointly with NTPC with an allocated geological reserve of 130 & 266 Million Tonnes respectively.
- Pursuant to the decision of the Board of Directors, JKSPDC engaged M/s SBICAPS as consultants to carry out the viability & sensitivity analysis of various options and accordingly advise on the way forward essentially with regard to location of the end use plant.
- SBICAPS has furnished a report which states that with a coal availability of 3.40 million tonnes per annum (assuming that extractable coal reserves would be 6070 % of geological reserve of 130 MT for 25 years), the installed capacity works out to 660 MW (supercritical unit).
- Net financial impact by locating the project in J&K vis-a-vis Odisha is estimated to be Rs.700 crore per annum which translates to over Rs.18000 crore over the lifetime of the project.
- JKSPDCL is yet to enter into JV with NTPC for both coal mining.
- Law Department has cleared the draft JV Agreement, which is expected to be signed soon.
Projects under Survey & Investigation through Swiss Challenge method
Pursuant to cabinet approval, JKSPDC has awarded 84 MW Shutkari Kulan & 100 MW Parkhachik Panikhar HEPs to M/s SP infra & M/s HCC respectively for development under Swiss Challenge method. While SP Infra has already commenced work, M/s HCC has withdrawn. Alternatives are being worked out.
Year wise capacity addition in 12th & 13th Five Year Plan |
S.No |
Name of Project |
Capacity
(MW) |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
2021 |
1 |
3rd Unit of Pahalgam |
1.5 |
1.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
BHEP-II |
450 |
|
|
450 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
Hanu HEP |
9 |
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
Dah HEP |
9 |
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
5 |
Parnai HEP |
37.5 |
|
|
|
|
37.5 |
|
|
|
|
6 |
Lower Kalnai |
48 |
|
|
|
|
48 |
|
|
|
|
7 |
New Ganderbal |
93 |
|
|
|
|
|
93 |
|
|
|
8 |
Sawalkote HEP |
1856 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1856 |
9 |
Kirthai- I |
390 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
390 |
|
|
10 |
Kirthai-II |
930 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
930 |
|
11 |
Large IPP (850 MW Ratle HEP) |
850 |
|
|
|
|
850 |
|
|
|
|
12 |
Small IPP |
376 |
25 |
|
|
45 |
|
200 |
106 |
|
|
13 |
TDP Pugah Geothermal |
5 |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
Joint Venture Projects |
2220 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
660 |
1560 |
|
15 |
Central Sector |
1679 |
329 |
|
|
330 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
8954 |
355.5 |
|
450 |
380 |
953.5 |
293 |
1156 |
2490 |
1856 |
1020 MW in Central Sector, 212 MW Ujh and Thermal Project not included in the projections. |
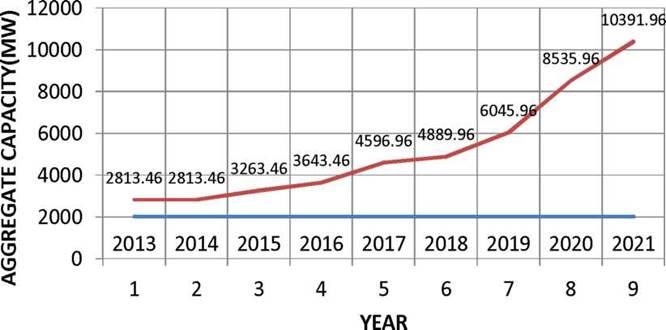
Road Map - Generation
A road map for capacity addition during 12th & 13th five year plan has been drawn as follows.
Sector wise break up of 57 Projects |
S.No. |
Sector |
Projects |
Capacity |
1. |
State Sector |
15 |
6263 MW( includes 3 Projects of JVC of 2220 MW) |
2. |
Central Sector |
5 |
1859( including Burser 1020 MW) |
3. |
IPP (Big) |
1 |
850 |
4. |
IPP (Small) |
36 |
372.50 |
Total |
57 |
9344.50 MW |
POWER TRANSMISSION
Present Scenario
The Transmission and Distribution of power is looked after by Power Development Department in the State of J&K. Effective and efficient Transmission and Distribution is as vital as the generation of power. The need of power in the State is growing, so does the generation. In order to transfer the Power from point of generation to point of consumption effectively, the Transmission and Distribution infrastructure needs development. The infrastructure of Transmission and Distribution serving the State consists of four transformation capacities of different voltage levels i.e. 220/132 KV level, 132/66-33 KV level, 66-33/11 KV level and 11/0.04 KV level.
Availability and Requirement of "Transmission & Distribution System" (MVA)
S.
No. |
Voltage level |
Availability of Grid capacity ending 201213 |
Availability of Grid capacity ending 201314 |
infrastructure required by
2016-17 Peak demand by end 2016-17 |
Gap to be met during 12th fyp |
1 |
220/132
KV level |
3570.0 |
3730.0 |
5160.00 |
1430 |
2 |
132/66-33
KV Level |
3973.0 |
4163.0 |
6192.00 |
2029 |
3 |
66-33/11
KV level |
4703.85 |
4891.30 |
7431.00 |
2539.7 |
4 |
11-6.6/0.4
KV level |
5388 |
5822.64 |
8917.00 |
3094.36 |
Total |
17634.85 |
18606.94 |
27700.00 |
9093.06 |
3730MVA transformation capacity was available at 220kV level and 4163MVA at 132kV level by the end of year 2013-14. The infrastructure available to meet the transmission of estimated demand at the end of 12th plan, is not adequate enough in the State. Hence there is an urgent need to upgrade the Transmission and Distribution infrastructure so that future needs of T&D can be fulfilled effectively. In the wake of thrust on Generation of more and more power in the State by undertaking the fresh projects, the need for such T&D network needs immediate attention. The infrastructure capacity required at 220/132kV level to meet the anticipated peak demand is 5160MVA ending 2016-17, there will be a gap of 1430MVA at the end of 12th five year plan which is to be met out in phased manner. Likewise the estimated requirement of transformation capacity at 132/66-33kV level at the end of 12th plan will be 6192.00 MVA leaving a gap of 2029MVA and at 66- 33/11kV level will be 7431 MVA leaving a gap of 2539.70MVA and at 11-6.6/0.4kV will be 8917 MVA leaving a gap of 3094.36MVA which is to be provided in phased manner during the 12th plan.
Around 9000 MW capacity generation is under execution under state sector, central sector, IPP mode and Joint Venture out of which around 2100 MW is scheduled to come up by the end of 12th five year plan. The state has to prepare evacuation system for this generation during 12th plan period which is scheduled to come by the end of 12th plan.
Transmission Capacity available
Capacity at 400 / 220 KV Level (MVA): Owned & operated by PGCIL AT 400kV level, availability at present is as under:
- Wagoora = 1260 MVA.
- New Wanpoh = 630MWA.
- KishenPur = 945MVA.
- Samba = 630MVA.
- TOTAL = 3465MVA.
|